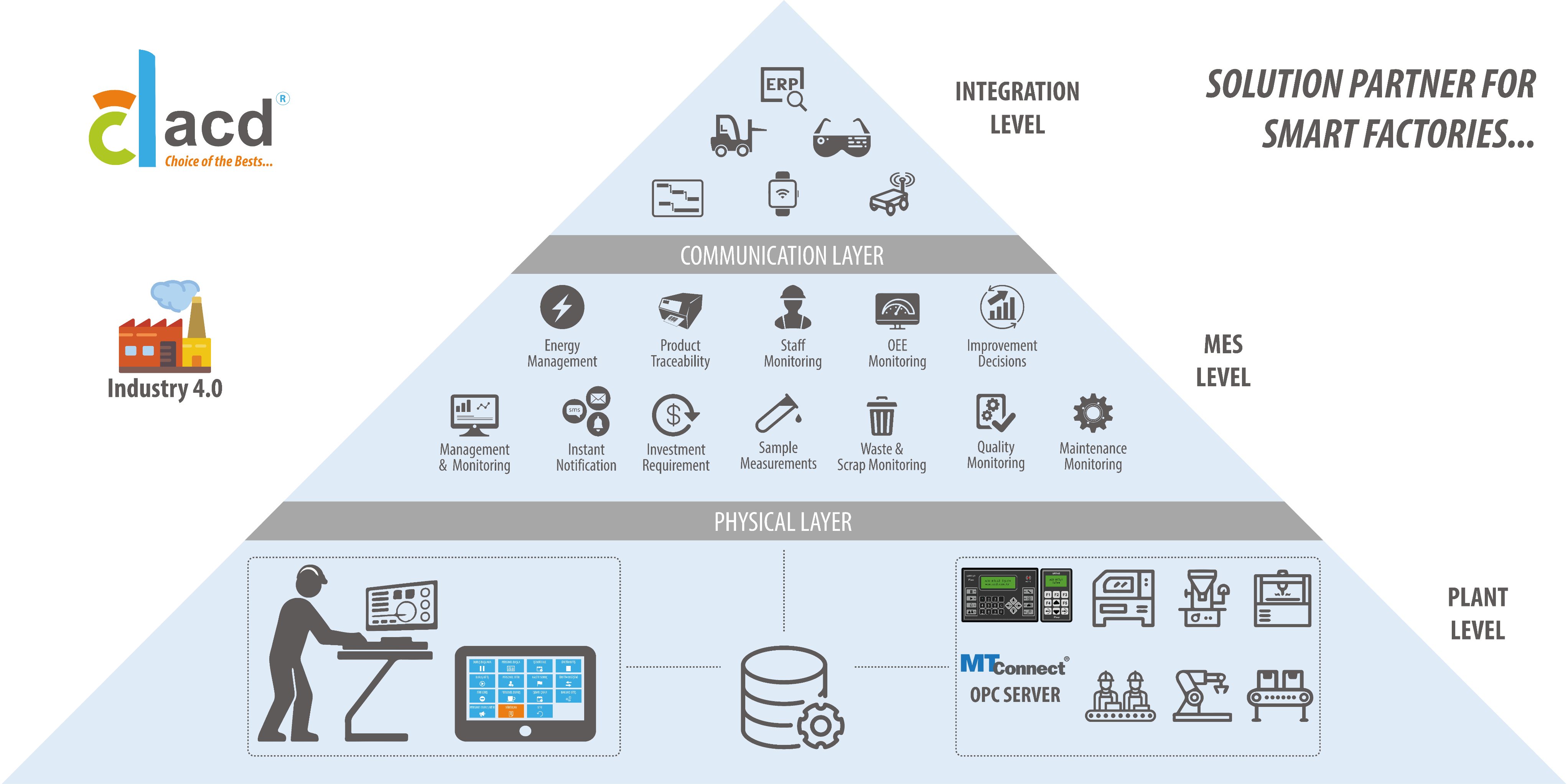
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are information technology products developed to maintain operations in production facilities in the best possible way and to ensure communication of production data. This system covers the process from the receipt of work order information until the product is completed and transferred to the warehouse, and records all activities in the production process, reports and analyzes them.< br/>
MES software includes data collection, analysis and reporting, detailed production and maintenance scheduling, assigning resources such as equipment and operators to jobs, monitoring the processes in the production stage, providing data feed to systems such as ERP, MRP, Maintenance Management System, Quality Management System. Quality, performance, maintenance and actual costs can be managed and capacity utilization can be measured with the help of activities within this scope.
The first and most important function of MES is to collect data from the production facility. This data is collected from equipment and locations.
In the light of the data obtained from the machines and the operators in charge of the machines, data such as start-finish times, cycle times, working speeds, quality rates, stopping reasons and durations, maintenance information are collected with MES. Risk management and preventive analyzes are also offered through the sensors on the machines and the signals from these sensors.
Information such as which order is currently being produced, at what stage the order is, how much of it has been completed in line with the data obtained from different types of locations such as non-equipment assembly, paint shop, source within the facility, and the performance values of these locations are obtained.
Data collected by MES are divided into real-time data and analysis data.
With real-time data, instant information is obtained in cases such as machine failure, waste increase, decrease in production efficiency. These notifications can be sent to the relevant units and responsible via SMS, E-mail or andon screens. The data where orders are made and showing the working status of jobs and operators are also included in real-time data.
Analysis data are reports that are presented to the user with different data processing techniques and evaluated in the short term or long term. Although it is thought that all reports need to be accessed instantly, it does not require monitoring as soon as a report is created, including long-term energy consumption data of the machines.
Another function of MES is to provide data to systems such as ERP, MRP, Maintenance Management System, Quality Management System and to increase the benefits to be obtained from these systems. For example, the sales team can see in which workshop, at what stage, and how much of the customer orders have been completed, instantly and precisely, thanks to MES data.
- MES initiates all production activities, guides them and provides reporting on the situation.
- With MES, you are informed about the instantaneous changes in the production process and it provides the opportunity to make appropriate interventions to these changes at the appropriate time. In this way, risks are managed, solutions can be sought as soon as problems arise, unworthy operations can be left and the performance of processes can be increased.
- With MES, overall equipment efficiencies can be reached instantly, capacity utilization rates can be optimized, unnecessary inventory levels decrease, turnover speeds increase, and profit margin and cash flow rate are improved.
- A double-sided flow of critical information between production planning and maintenance planning is provided with MES.
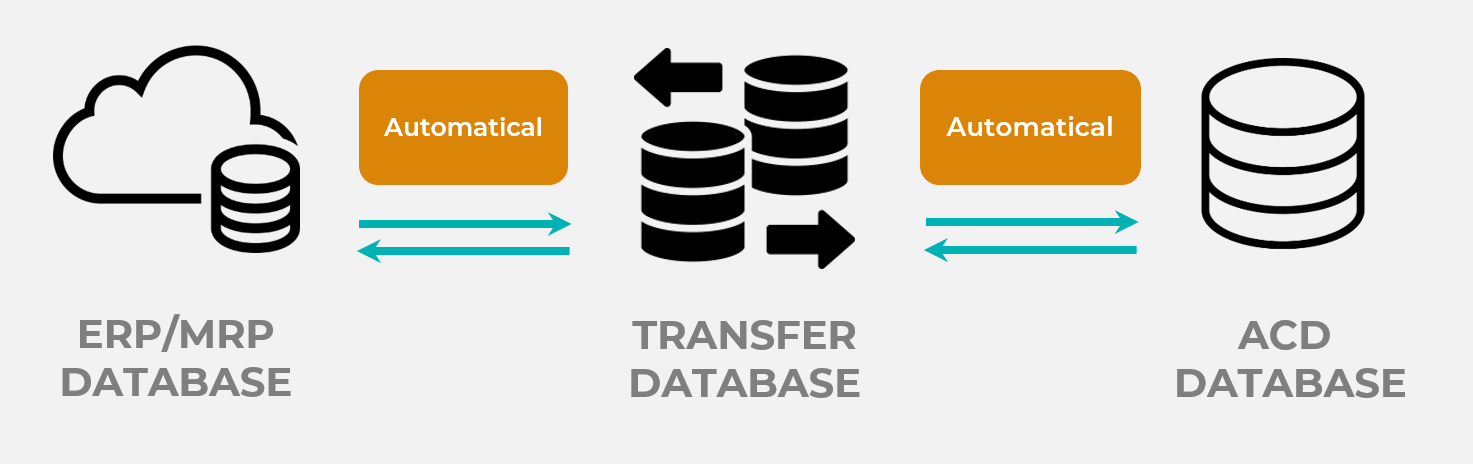
- Production definitions such as work orders, personnel information, machine information, stopping reasons that occur in ERP are taken into the MES software. The production data (production times and results, consumed raw material quantities, order statuses, operator performances) generated in the MES software are also transferred to the ERP system.
- There is a bidirectional integration between ERP and MES and this integration automatically transfers data (at certain time periods, user-independent).
- At the same time, MES software works in integration with PDKS, Maintenance Management System, Quality Management Systems used in production facilities and data exchange takes place between these systems.